实用优化算法(六-1)Selection in Genetic Algorithm
- 14-11-18
- Algorithm
- algorithm
遗传算法包括三个基本操作选择、交叉、变异,这一篇说说选择(Selection)
##轮盘赌选择(Roulette Wheel Selection)
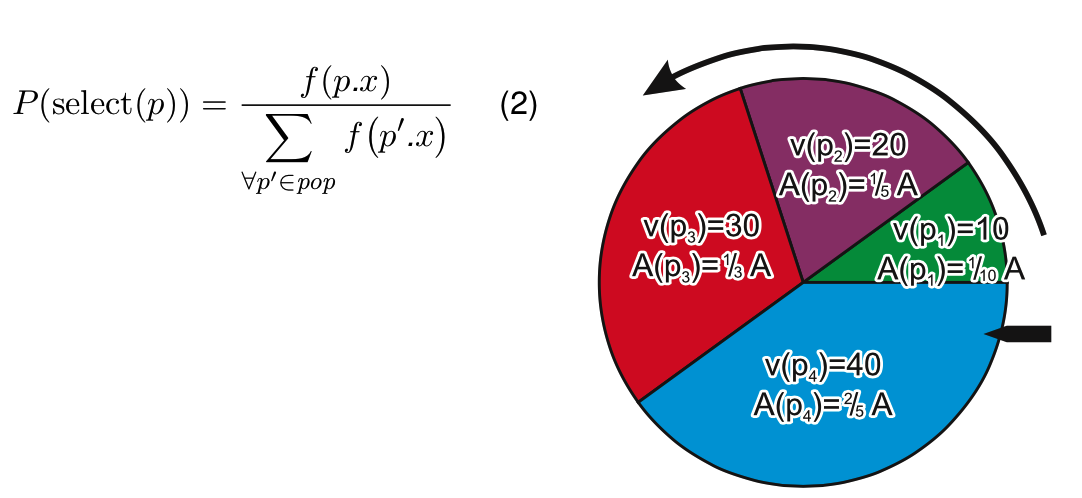
轮盘赌选择法可用如下过程来模拟实现:
1、在[0,1]内产生一个均匀分布的随机函数 r
2、如果 r <= q1,则染色体 x1 被选中。
3、若 qk - 1 < r <= qk (2<=k<=N),则染色体 xk 被选中,其中qi为染色体xi(i=1,2,…,n)的累积概率,计算公式为:
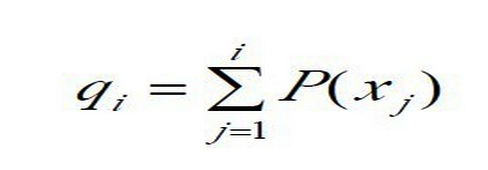
这里我们举一个简单的例子就可以明白累积概率的问题!
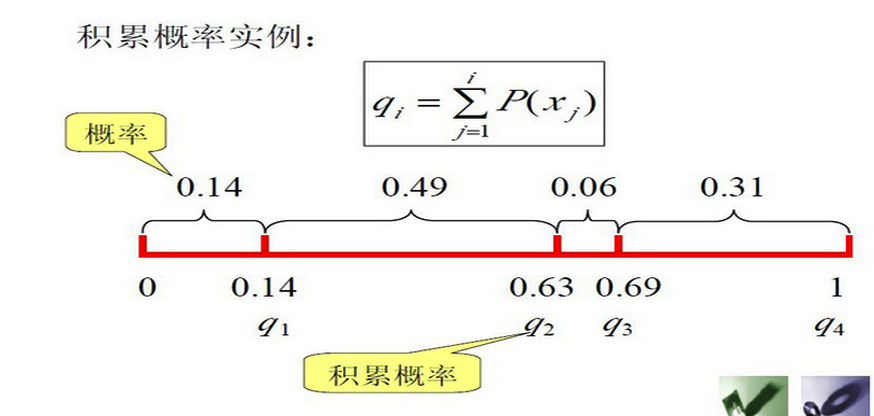
这样我们就可以将所有个体的获取概率均匀分布在[0,1]的范围内,通过生成一个[0,1]的随机数判断它在哪个区间而决定选择对象!
轮盘赌算法的实现步骤:
public class RouletteWheelSelection implements ISelectionAlgorithm {
private double[] temp;
public RouletteWheelSelection() {
super();
}
@Override
public void select(final Individual<?, ?>[] pop, final Individual<?, ?>[] mate, final Random r){
double[] t;
double max, last;
int i, j;
//将上一次使用轮盘赌算法得到的初始化数组赋值给 t
t = this.temp;
//如果是第一次使用轮盘赌选择法或问题空间发生变化,那么初始化 t 和 temp
if ((t == null) || (t.length < pop.length)) {
this.temp = t = new double[pop.length];
}
max = Double.NEGATIVE_INFINITY;
//找到个体中适应值最大的
for (Individual<?, ?> indi : pop) {
max = Math.max(indi.v, max);
}
max = Math.nextUp(max);
last = 0d;
//计算每个个体的适应值的累积概率,并存储在数组 t 中
for (i = 0; i < t.length; i++) {
last += (max - pop[i].v);
t[i] = last;
}
//确保最大累积概率,个体的累积概率永远不会超过最大累积概率
t[t.length - 1] = Double.POSITIVE_INFINITY;
//交配个体选择
for (i = 0; i < mate.length; i++) {
//last 中存储了累积概率的总和
//在累积概率数组 t 中搜索对应值 last * r.nextDouble,如果找到,那么返回对应的索引值
//如果没有找到并且 last * r.nextDouble 小于 t 中的一个或多个元素,返回一个负数(大于该值的第一个元素的索引的按位求补)
//如果没有找到并且 last * r.nextDouble 大于 t 中的所有元素,返回一个负数(虽有一个元素索引加1的按位求补),这种情况已经排除在外!
j = Arrays.binarySearch(t, last * r.nextDouble());
//选择 last * r.nextDouble 最接近的个体的索引值
if (j < 0) {
j = ((-j) - 1);
}
//将旋转赌轮盘一次得到的个体纳入交配池
mate[i] = pop[j];
}
}
}
##锦标赛选择(Tournament Selection) 锦标赛选择法的原理非常简单,k 个个体竞争一个进入交配池的机会,当然是适应度值最高的个体被选中!
public class TournamentSelection implements ISelectionAlgorithm { // start
//k 表示从 k 个个体中选择一个进入交配池
public final int k;
public TournamentSelection(final int s) {
super();
this.k = s;
}
@Override
public void select(final Individual<?, ?>[] pop, final Individual<?, ?>[] mate, final Random r) {
//交配个体选择
for(int i = 0; i < mate.length; i++) {
int a = r.nextInt(pop.length);
//从 k 个随意选择的个体中选取适应性最强的个体进入交配池
for(int j = 1; j < k; j++ ){
int b = r.nextInt(pop.length);
if(pop[b].v > pop[a].v){
a = b;
}
}
mate[i] = pop[a];
}
}
}
##截断选择(Truncation Selection) 截断选择的思想很简单,就是从全部种族个体中选择 mps 个最优秀的个体进入交配池, mps 总是小于种族个体总数 ps。
public class TruncationSelection implements ISelectionAlgorithm {
public static final TruncationSelection INSTANCE = new TruncationSelection();
private TruncationSelection() {
super();
}
@Override
public void select(final Individual<?, ?>[] pop, final Individual<?, ?>[] mate, final Random r) {
//对 pop 中的所有个体进行排序(默认从小到大-升序排列)
Arrays.sort(pop);
//复制 pop 数组中从 0~mate.length 的数据 到 mate 数组中 0~mate.length
System.arraycopy(pop, 0, mate, 0, mate.length);
}