实用优化算法(七)解决商人旅行问题(TSP)
- 14-11-25
- Algorithm
- algorithm
##Traveling Salesman Problem(TSP) 首先让我们回顾一下TSP问题:一个商人想要以最短时间访问n个城市,每个城市只能去一次,并且最终将回到他出发的城市。
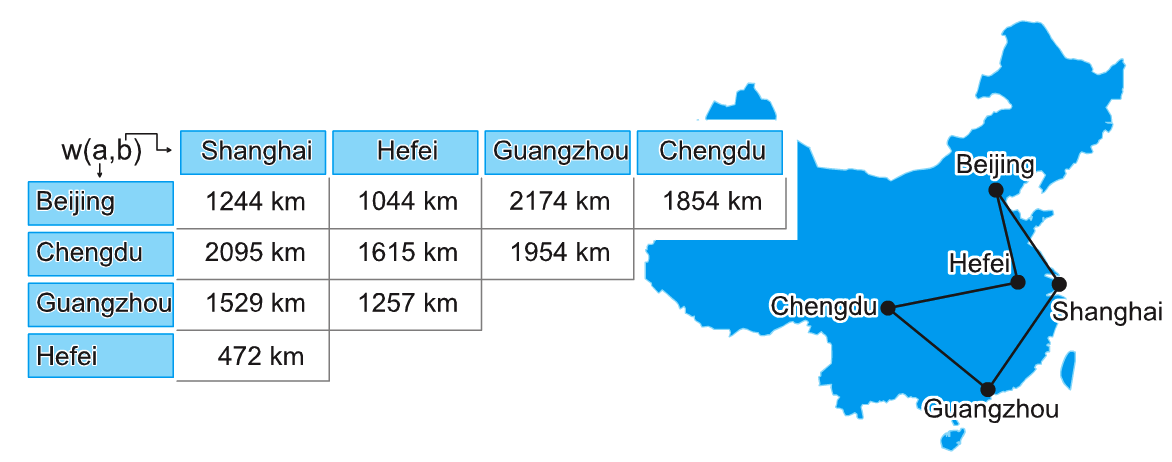
问题空间:X = Π { Beijing , Chengdu , Guangzhou , Hefei , Shanghai }
目标函数:Minimize f (x) = dist( Hefei , x[0]) + Σ(i=0->2)dist(x[i] , x[i + 1])+dist(x[3] , Hefei )
public class TSPProblem implements IObjectiveFunction<int[]> {
//使用二维数组记录每两个城市之间的距离
private double[][] m_cities;
public TSPProblem() {
super();
}
//从一个文件中读取TSP问题的距离列表
public final void readResource(final String r) throws IOException {
try (InputStream x = TSPProblem.class.getResourceAsStream(r)) {
this.readStream(x);
}
}
//返回城市的数目
public final int cityCount() {
return this.m_cities.length;
}
//计算两个城市之间的距离
public final double dist(final int a, final int b) {
double x, y;
x = (this.m_cities[a][0] - this.m_cities[b][0]);
y = (this.m_cities[a][1] - this.m_cities[b][1]);
return Math.sqrt((x * x) + (y * y));
}
//计算拟定路径的总长度
@Override
public final double compute(final int[] x) {
double s;
int prev;
prev = x[x.length - 1];
s = 0;
for (int cur : x) {
s += this.dist(prev, cur);
prev = cur;
}
//return the total distance of the travel
return s;
}
}
计算路程总和的函数我们已经有了,在TSP问题中我们可以测试并比较所有的路径长度吗?答案肯定是不可以!对于TSP问题,问题空间的大小可是|X|=0.5*(n-1)!
那我们怎么去解决这个问题呢?
##关于TSP所采用的gpm详解 TSP的问题空间为X = Π { Beijing , Chengdu , Guangzhou , Hefei , Shanghai },在共同启发式演算法中,TSP问题的表现型就是它的问题空间,我们可以将问题空间转化为搜索空间G = Π { 0 , 1 , 2 , 3 , 4 },即它的基因型。
使用基因型代替表现型的好处是:可以将目标函数和元启发式相结合产生一个抽象并且有效的方式作为一个黑盒程序。
接下来将阐述登山算法(Hill Climbing)是如何解决TSP问题的:
//使用Nullary方法生成一个随机的一维数组序列作为初始序列
best.g = nullary.create(this.random);
//通过gpm将基因型映射为表现型
best.x = this.gpm.gpm(best.g);
//使用TSP问题的solve函数计算出该表现型序列对应的路程总和
best.v = f.compute(best.x);
//迭代,
while(!(this.termination.shouldTerminate())){
//修改最佳候选结果的基因序列,得到新的候选结果
pnew.g = this.unary.mutate(best.g, this.random);
//将该基因型映射到表现型
pnew.x = this.gpm.gpm(pnew.g);
//计算出该新候选结果对应的路程总和
pnew.v = f.compute(pnew.x);
//如果新的候选结果路程总和小于最佳候选结果的路程总和
if( pnew.v <= best.v){
//将新候选结果作为最佳候选结果
best.assign(pnew);
}
}
##关于TSP所采用的Search Operation 对于TSP问题,Nullary方法为产生一个值与序号相对应的一维数组
public class PermutationNullaryUniform implements INullarySearchOperation<int[]> {
public final int n;
//参数num为TSP问题中的城市个数,作为数组的长度
public PermutationNullaryUniform(final int num) {
super();
this.n = num;
}
@Override
//仅仅是简单的初始化一个一维数组,值于序号相对应
public int[] create(final Random r) {
final int[] g;
g = new int[this.n];
for(int i = 0; i < this.n; i++ ){
g[i] = i;
}
return g;
}
}
Unary方法是一个变异的过程,通过随机改变一维数组的序列来产生新候选结果的基因型
public class PermutationUnarySingleSwap implements IUnarySearchOperation<int[]> {
@Override
public int[] mutate(final int[] p, final Random r) {
final int[] g;
g = p.clone();
int n = g.length;
//随机选择两个元素
int i = r.nextInt(n);
int j = r.nextInt(n);
while (i == j){
j = r.nextInt(n);
}
//交换
int t = g[i];
g[i] = g[j];
g[j] = t;
return g;
}
}
##使用登山算法解决TSP
public class HCOnTSP {// start
public static void main(final String[] args) throws IOException {
final TSPProblem problem = new TSPProblem();
problem.readResource("tsp100.txt");
//创建并初始化算法实例
final HC<int[], int[]> algorithm;
algorithm = new HC<int[], int[]>();
//定义TSP问题所需的Nullary和Unary方法,这里使用的是一维数组
algorithm.nullary = new PermutationNullaryUniform(problem.cityCount());
algorithm.unary = new PermutationUnarySingleSwap();
//确定使用HC算法获得候选结果的个数,循环一次得到一个候选结果
for (int i = 1; i <= 25; i++) {
//定义终止条件
algorithm.termination = new MaxSteps(20000);
//输出结果,algorithm.solve(problem).v的值为路程长度
System.out.println(algorithm.solve(problem).v);
}
}
}