实用优化算法(十四)基因编程(Genetic Programming)
- 14-12-24
- algorithm
- algorithm
##什么是基因编程
基因编程是一种进化算法。基于人口的优化算法;过程迭代(每一代);每一代人口经历适者生存淘汰;被选中的个体通过变异和重组再繁殖
那么与基因算法(Genetic Algorithm)、进化策略(Evolution Strategy)和微分进化(Differential Evolution)的差别是什么呢?
它进化程序或者树结构或者图表结构
##回归符号
给一系列点的集合 S = {(x1, y1),(x2, y2), . . . ,(xn, yn)}
找出函数表达式 ϕ : R → R
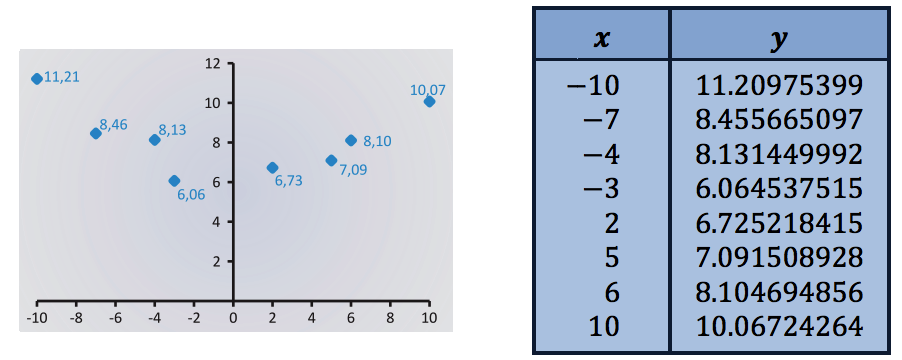
因此我们需要使用基因编程得到回归到符号表达式:
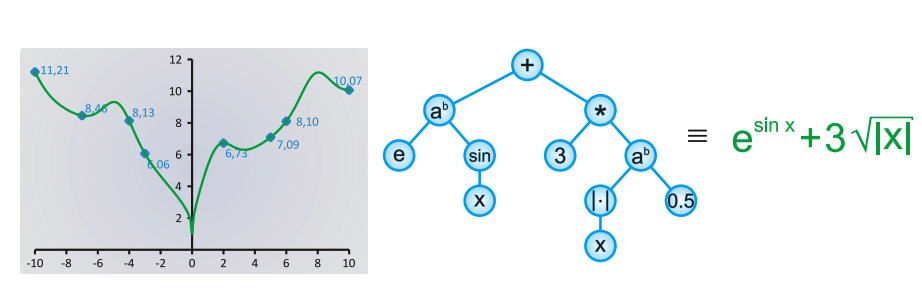
1、使用树结构表现表达式
2、例如 minimize f(ϕ) = Σ (yi − ϕ(xi))^2
3、使用基因编程构造 ϕ
符号复原的思想
一系列点的集合 S = {(x1, y1),(x2, y2), . . . ,(xn, yn)};
函数集 F = {+,-,*,sin,exp…}
叶子节点集 包括变量 x 和实数集 T = {x,R,…}
我们需要找到的是一个有 F、T中元素所组成的一个符合数据的表达式
##基因编程
进化算法:
以随机程序开始;
测试个体特征;模拟性能加标准条件(比如:size);
适应性可以使相关的,决定了其后代的个数;v(ϕ) 符号回归中的适应性可以是,square error f(ϕ) v(ϕ) = f(ϕ) +penalty ∗ size(ϕ)
变异操作是插入一个随机的子树,重组操作是交换子树。
##树的构建
方法一:最大深度构建——添加随机的函数节点到深度 maxDepth-1,最后添加叶子节点
方法二:增长式构建——随机添加函数或者叶子节点,知道所有的树枝都终结,或者达到深度 maxDepth - 1,最后添加叶子节点到所有树枝
方法三:各一半——一半节点采用方法一,一半节点采用方法二
##臃肿(Bloat)
臃肿就是程序无控制的增长
臃肿当然是不好的,高雅的结果总是简单而又小巧,大的程序等于很长的运行时间,运作和评估的增长;大的程序会导致过度的危险;大的程序当然占据很大的内存空间
应对措施:
使用多对象优化;在单对象优化中采取惩罚;设置程序大小的上限;使用特别的变异和交叉操作
##基因编程的实现
public class SymbolicRegressionGP {
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public static void main(final String[] args) throws IOException {
final EA<RealFunction, RealFunction> ea = new EA<>(); // 调用进化算法解决基因编程问题
final NodeTypeSet<RealFunction> nts;
final NodeTypeSet<RealFunction>[] binary, unary;
final IObjectiveFunction<RealFunction> f;
nts = new NodeTypeSet<>(); // 符号集
binary = new NodeTypeSet[] { nts, nts }; // a binary function has two child elements
unary = new NodeTypeSet[] { nts }; // a unary function has only one
// 自定义添加符号集
nts.add(new ReflectionNodeType<>(Sin.class, unary)); // we use: sine
// choose more mathematical operators from package poad.G.trees.data.math
// and its sub-packages
// see class oad.examples.lesson_10.SymbolicRegressionGP: it is an example
// 定义为二叉树
nts.add(new VariableType(2)); // 2 dimensions!
f = new SymbolicRegressionObjective(
// 在其中添加已知的 输入-输出 对
new DataPoint(new double[] {/** input values x1, x2*/}, /** measured output y */), //
);
ea.nullary = new TreeRampedHalfAndHalf<>(nts, 6); // Ramped-Half-and-Half: max depth 6
ea.unary = new TreeMutator<>(6); // the tree mutator: max depth 6
ea.binary = new TreeRecombination<>(6); // binary search operation (crossover)
ea.ps = 256; // set population size to some good value
ea.mps = 128; // set mating pool size to some good value
ea.selection = TruncationSelection.INSTANCE; // use truncation selection
ea.cr = 0.3; // set crossover rate to some good value
for (int i = 1; i <= 100; i++) { // let's do 100 runs
ea.termination = new MaxSteps(1000000); // for each run, allocate 1'000'000 steps
Individual<RealFunction, RealFunction> res = ea.solve(f); // invoke optimizer
System.out.println("run " + i + //$NON-NLS-1$
" has result quality " + res.v + " and result " + res.x.toString()); //$NON-NLS-1$
}
}
}