实用优化算法(十二)微分进化(Differential Evolution)
- 14-12-21
- algorithm
- algorithm
微分进化(Differential Evolution) 是针对实数优化问题的简单进化算法,搜索空间(Search space)是实数 G = Rn.
核心思想是: 三元重组操作代替了变异和二元交叉
人口操作:每个后代与他的直接父代竞争,如果适应性强则直接取代。
其余部分与 EA(进化算法)相同
##通过自组织来自适应
我们有三种适应算法:
1、随着时间不断独立于搜索过程的改变参数。比如:模拟退火算法
2、根据某些使用有关搜索进展的信息来改变参数。比如:使用1/5th 的进化策略
3、将参数作为附加参数编码作为个体的记录,并让进化算法通过选择和繁殖来适应。比如:使用内因方法的进化策略
只有后两个是自适应方法,因为他们的行为并不是由算法设计者所提前预料设计的。
自适应自组织算法是不需要参数的!
##三元繁殖操作
微分进化使用单一三元繁殖操作——RecombineDE,需要三个参数 g1, g2和 g3
recombineDE(g1,g2,g3) = g3 + F(g1 - g2)
开始,所有候选结果均匀分布在搜索空间G中;微分信息(g1-g2)很大,那么搜索步长就大;
随着人口收敛,后续按结果之间的距离变的更近;距离(g1-g2)减少,搜索步长减小;
自适应的整个过程不需要任何附加参数。
步长根据人口的结构自组织,根据优化过程自适应
##例子 例1:
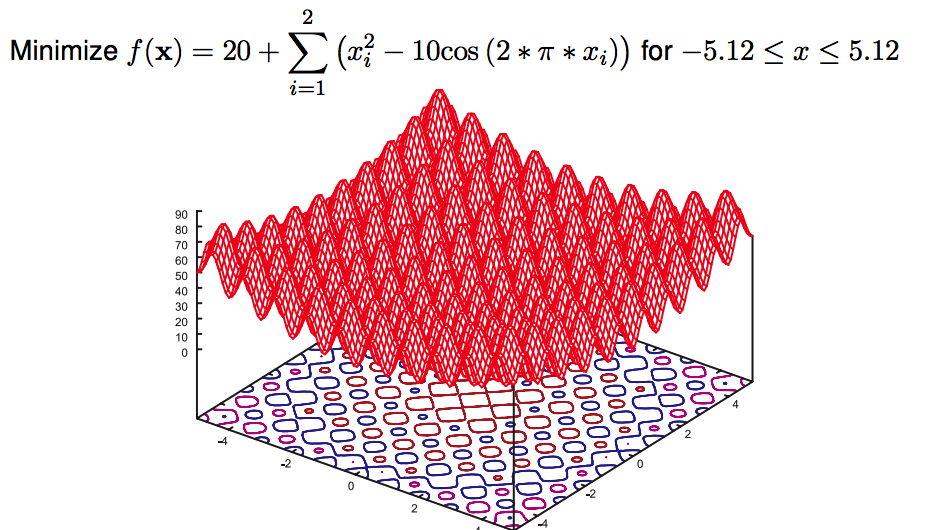
人口初始化均匀分布,人口之间微分信息差异很大;
当人口开始收敛到局部优化,后续按结果之间的距离变得越来越近,微分信息的差异变小了;
由于是不同的优化,微分信息依旧可用
例2:
recombineDE(g1, g2, g3) = g3 + F (g1 − g2)
g1 = (0.3, 0.45, 0.7)T
g2 = (0.2, 0.5, 0.7)T
g3 = (0.25, 0.4, 0.6)T
F = 0.3 ←− strength parameter
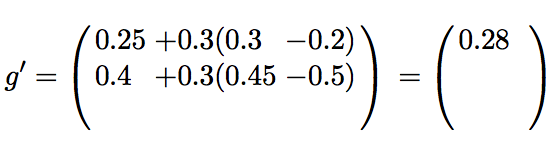
##DE Recombination
三元 DE Recombination 方法
public double[] recombine(final doublep[] g1, final doublep[] g2, final double[] g3, final Random r){
double[] res;
int i;
double x;
res = g3.clone();
for(i = g3.length; (--i) >= 0;){
if(r.nextDouble() <= this.cr){
//this.F是强度参数
x = res[i] + (this.F*(g1[i] - g2[i]));
if((this.min < x) && (this.max > x)){
res[i] = x;
}
}
}
return res;
}
DE Algorithm
public class DE<X> extends OptimizationAlgorithm<double[], x>{
public ITernarySearchOperation<double[]> ternary;
public int ps;
public DE(){
super();
this.ps = 16;
}
@Override
@SupperssWarning("unchecked")
public Individual<double[], X> solve(final IObjectFunction<X> f){
Individual<double[], X>[] parent, children;
Individual<double[], X> current, best;
int i, j, k;
parents = new Individual[this.ps];
children = new Individual[this.ps];
best = new Individual<>();
//初始化人口
for(i = children.length; (--i) >= 0){
children[i] = current = new Individual<>();
current.g = this.nullary.create(this.random);
}
for(;;){
//构建父代人口基数
for(i = children.length;(--i) >= 0){
current = children[i];
current.x = this.gpm.gpm(current.g);
current.v = f.compute(current.x);
//如果是第一代或者子代优于父代,将当前子代直接取代父代
if(parents[i] == null || current.v <= parents[i].v){
parents[i] = current;
if(best == null || best >= current.v){
best = current;
}
}
if(this.termination.shouldTerminate()){
return best;
}
}
//基因交流,交配产生后代
for(i = children.length; (--i) >= 0;){
do{
j = this.random.nextInt(children.length);
}while(j == i);
do{
k = this.random.nextInt(children.length);
}while(j == k || k == i);
children[i] = current = new Individual<>();
//三元重组
current.g = this.ternary.recombine(parents[i].g, parents[j].g, parents[k].g, this.random);
}
}
}
}
##Gene-wise Recombination
修改:等式并没有一次性应用到所有的基因上。而是一个基因交叉率 cr 被用来决定哪个基因应该参与竞争
其余的都是直接从 g3 复制来
两个基本的方法:
1、binomial:对于后代的每一个基因,使用概率 cr 下的等式7 和 g3中相应的 1-cr 概率的值
2、exponential:对每一连续组基因使用等式7,根据 cr 使用指数分布的长度;其他的从 g3 复制