实用优化算法(十三)解决UglyFunction问题
- 14-12-22
- algorithm
- algorithm
##介绍 最小化丑陋的函数式问题:有一个在实数[-10,10]^10 十维空间的丑陋函数式,我们的目标是要找到它的最小值。换句话说,我们需要找到一个十维向量 x,可以让函数 f(x) 得到一个最小的可能结果。
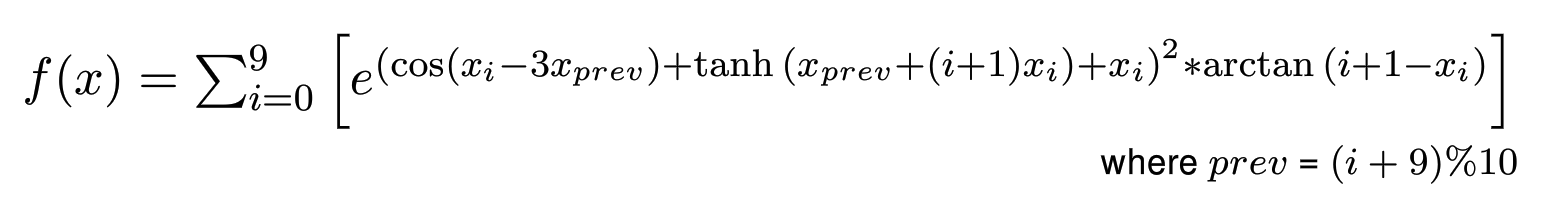
今天,我们就是尝试使用多种方法解决 UglyFunction 问题。
慢着,我们似乎已经学过进化策略,对于数值问题,我们是不是应该使用进化策略中的一些方法呢?!
问题空间:Rn [-10,10]^10
目标函数:既是UglyFunction本身
##使用HC解决UglyFunction
GMP:使用登山算法 基因型与表现型完全相同
搜索操作:
Nullary:初始化候选结果
public final class RnNullaryUniform extends Rn implements INullarySearchOperation<double[]> {// start
public RnNullaryUniform(final Rn def) {
super(def);
}
@Override
public final double[] create(final Random r) {
final double[] g = new double[this.dim];
//随机构建一个长度为10的数组(候选结果为10维向量)
for (int i = g.length; (--i) >= 0;) {
//将每个元素随机赋值为 -10~10 的双精度浮点数
g[i] = (this.min + (r.nextDouble() * (this.max - this.min)));
}
return g;
}
}
Unary:变异候选结果
public class RnUnaryNormal2 extends Rn implements IUnarySearchOperation<double[]> {
public RnUnaryNormal2(final Rn def) {
super(def);
}
@Override
public double[] mutate(final double[] genotype, final Random r) {
double d;
final double[] g = genotype.clone();
for (int i = g.length; (--i) >= 0;) {
//使用进化策略中的正态分布变异 B 方法
do {
d = (g[i] + (r.nextGaussian() * (this.max - this.min) * 0.01d));
} while ((d < this.min) || (d > this.max));
g[i] = d;
}
return g;
}
}
调用HC解决UglyFunction:
public static void main(final String[] args) throws IOException {
final HC<double[], double[]> hc = new HC<>(); // create HC
final UglyFunction problem = new UglyFunction(); // the problem/objective
//Rn 表示了在 -10~10 之间,维度为 10
final Rn rn = new Rn(-10d, 10d, 10);
//定义搜索操作
hc.nullary = new RnNullaryUniform(rn); // instantiate nullary search operation
hc.unary = new RnUnaryNormal2(rn); // instantiate unary search operation
for (int i = 1; i <= 100; i++) { // let's do 100 runs
hc.termination = new MaxSteps(1000000); // for each run, allocate 1'000'000 steps
Individual<double[], double[]> res = hc.solve(problem); // invoke optimizer
System.out.println(res.v + " from " + Utils.toString(res.x));
}
}
##使用EA解决UglyFunction
Search Operations:
Nullary:随机生成 dim*40 的二进制流数组
Unary:随机选择一位翻转该值
binary:使用组合式交叉法
调用EA:
public class EAOnUglyFunction {
public static void main(final String[] args) throws IOException {
final EA<boolean[], double[]> ea = new EA<>(); // create EA
final UglyFunction problem = new UglyFunction(); // the problem/objective
final Rn rn = new Rn(-10d, 10d, 10);
ea.nullary = new BitsNullaryUniform(rn.dim*40); // 初始化nullary搜索操作
ea.unary = new BitsUnaryFlip(); // 初始化unary搜索操作 (变异)
ea.binary = new BitsBinaryUX(); // 初始化二进制搜索操作(交叉)
ea.ps = 48; // 设置人口基数
ea.mps = 16; // 设置交配池的大小
ea.selection = TruncationSelection.INSTANCE; // 选用截断算法
ea.gpm = new BitsToDoublesGPM(rn); // 使用双精度浮点数到二进制位流的映射方法
ea.cr = 0.3; // 设置交叉概率为 0.3
for (int i = 1; i <= 100; i++) { // let's do 100 runs
ea.termination = new MaxSteps(1000000); // for each run, allocate 1'000'000 steps
Individual<boolean[], double[]> res = ea.solve(problem); // invoke optimizer
System.out.println(res.v);
}
}
}
##使用ES解决UglyFunction
Search Operations:
Nullary:随机生成长度为10的 值的大小在 -10~10 之间的双进度浮点数。
Unary: 根据参数列表中的 sigma 使用进化策略的变异法 即:x = genotype[i] + sigma * r.nextGaussian()
调用ES解决UglyFunction:
public class ESOnUglyFunction {// start
public static void main(final String[] args) throws IOException {
final ES1P1<double[]> es = new ES1P1<>(); // create ES
final UglyFunction problem = new UglyFunction(); // the problem/objective
final Rn rn = new Rn(-10d, 10d, 10);
es.nullary = new RnNullaryUniform(rn); // instantiate nullary search operation
es.unary = new RnESUnaryNormal(rn); // 正态分布变异法
es.a = 0.95; // 设置变异强度变化的步长乘数为 0.95
es.L = 50; // 设置每50次迭代后进行一次适应性调整
es.sigma0 = 5; // 设置初始化变异强度为 5
for (int i = 1; i <= 100; i++) { // let's do 100 runs
es.termination = new MaxSteps(1000000); // for each run, allocate 1'000'000 steps
Individual<double[], double[]> res = es.solve(problem); // invoke optimizer
System.out.println("run " + i + //$NON-NLS-1$
" has result quality " + res.v +
" and result " + Arrays.toString(res.x)); //$NON-NLS-1$
}
}
}
##使用DE解决UglyFunction
public class DEOnUglyFunction {
public static void main(final String[] args) throws IOException {
final DE<double[]> de = new DE<>(); // create ES
final UglyFunction problem = new UglyFunction(); // the problem/objective
final Rn rn = new Rn(-10d, 10d, 10);
de.nullary = new RnNullaryUniform(rn);
de.ternary = new RnRecombineDE(rn,0.5); // 设置三元组合方法
for (int i = 1; i <= 100; i++) { // let's do 100 runs
de.termination = new MaxSteps(1000000); // for each run, allocate 1'000'000 steps
Individual<double[], double[]> res = de.solve(problem); // invoke optimizer
System.out.println("run " + i + //$NON-NLS-1$
" has result quality " + res.v +
" and result " + Arrays.toString(res.x)); //$NON-NLS-1$
}
}
}